Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, and heart stroke are two significant health concerns that are closely intertwined. Understanding the relationship between hypertension and heart stroke is crucial for promoting heart health and preventing life-threatening events. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the connection between hypertension and heart stroke, exploring the risk factors, mechanisms, and preventive measures.
Understanding Hypertension and Heart Stroke:
Hypertension is a condition characterized by elevated blood pressure levels, placing increased strain on the heart and blood vessels. Heart stroke, also known as a stroke or cerebrovascular accident (CVA), occurs when the blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, leading to damage or death of brain cells.
The Link Between Hypertension and Heart Stroke:
Hypertension is a leading risk factor for heart stroke, contributing to the development of ischemic strokes, which occur when a blood clot blocks an artery supplying blood to the brain. Several mechanisms explain the relationship between hypertension and heart stroke:
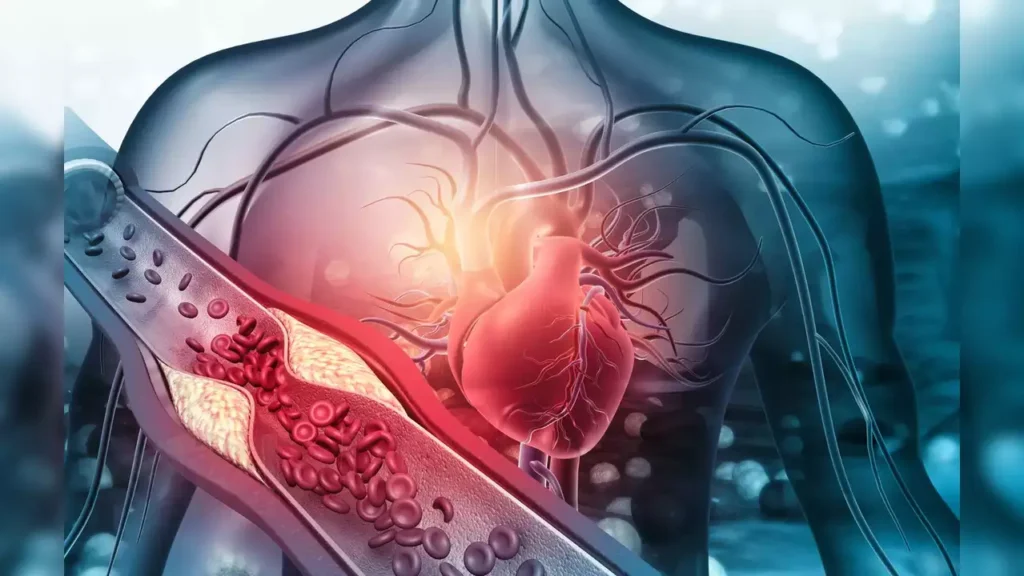
Damage to Blood Vessels: Chronic hypertension damages the walls of blood vessels, making them more susceptible to the formation of blood clots or plaque buildup, which can lead to stroke.
Increased Risk of Atherosclerosis: Hypertension accelerates the progression of atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of fatty deposits (plaque) in the arteries. Atherosclerosis narrows the arteries and increases the risk of blood clots, contributing to stroke risk.
Hypertensive Crisis: Acute elevations in blood pressure, known as hypertensive crises, can trigger a stroke by causing rupture or leakage of blood vessels in the brain.
Preventing Heart Stroke in Hypertensive Individuals:
Managing hypertension effectively is key to reducing the risk of heart stroke and promoting heart health. Here are some strategies for preventing heart stroke in hypertensive individuals:
Blood Pressure Control: Maintaining blood pressure within a healthy range through lifestyle modifications and, if necessary, medication management is crucial for reducing the risk of stroke.
Medication Adherence: Consistently taking prescribed medications for hypertension as directed by a healthcare provider is essential for controlling blood pressure and preventing complications.
Healthy Lifestyle: Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, including regular physical activity, a balanced diet low in sodium and saturated fats, maintaining a healthy weight, limiting alcohol consumption, and avoiding smoking, can help manage hypertension and reduce the risk of stroke.
Regular Monitoring: Regular blood pressure monitoring and follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are important for tracking progress, adjusting treatment as needed, and addressing any concerns.
Hypertension and heart stroke are closely linked, with hypertension being a significant risk factor for stroke. Understanding the relationship between hypertension and heart stroke and taking proactive steps to manage hypertension effectively through lifestyle modifications and medication management is crucial for promoting heart health and reducing the risk of stroke-related complications. By prioritizing blood pressure control and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, individuals can take control of their health and reduce their risk of heart stroke.






